dam is a constructed barrier that holds back water and raises its level. The important uses of dams have made it a matter of great concern for human civilization.

What are Dams Used for
There are many dams in this civilized world. Although the main function of these dams is to hold water back, they often provide additional useful facilities. Major dam uses are discussed below.
-
Water Supply
- Water stored in reservoirs of the dam is used to provide adequate amounts of quality freshwater to residential, industrial facilities and mining sites.
- Dams can be used to regulate the flow of water in rivers. This is to say that water can be released from the reservoir to support wildlife and ecosystems downstream during a drought, and water can be released for agricultural uses during the same drought.
- Example: Warragamba, a water supply dam of Australia, supplies water to more than 3.7 million people living in Sydney and the lower Blue Mountains.
-
Irrigation
- In many countries, cropland irrigation is done using water stored behind dams.
- Example: Burrinjuck Dam, an irrigation dam of Australia, which was built as the main headwater storage for the Murrumbidgee Irrigation Area in New South Wales.
-
Electrical Generation
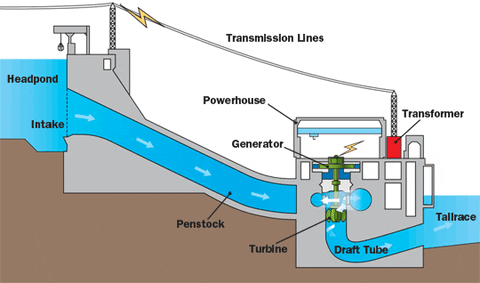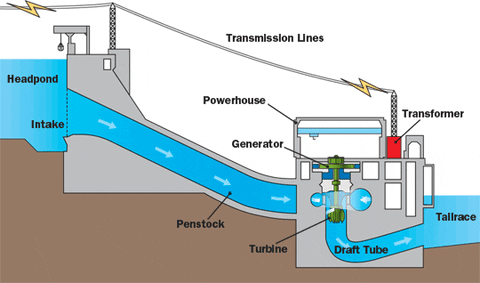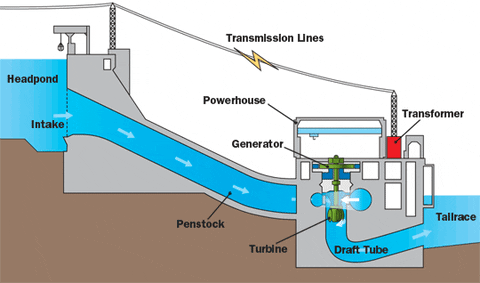
- To generate electricity in hydroelectric power stations
- Hydropower is considered clean because it does not contribute to global warming, air pollution, acid rain, or ozone depletion.
- The United States is one of the largest producers of hydropower in the world, second only to Canada. Dams produce over 103,800 megawatts of renewable electricity and meet 8 to 12 percent of the Nation's power needs.
- Example: Itaipu Dam, a hydropower dam in Brazil, is the largest hydro-electric power station in the world.
-
Flood Control
- For centuries, people have built dams to help control devastating floods. It helps to prevent the loss of life and property. Flood control dams impound floodwaters and then either release them under control to the river below the dam or store or divert the water for other uses.
- Example: The Tennessee Valley Authority dams in the U.S.A., help to control floods on the Tennessee, the lower Ohio, and the lower Mississippi Rivers.
-
Water Storage
- Dams create reservoirs that supply water for uses, including industrial, municipal, and agricultural.
- Water captured during the wet season can be stored for use during the dry season.
- Example: Corin Dam is a Water Storage dam of Australia which has a capacity of 19.9×109 gal.{adselite}
-
Mine Tailings
- It allows the mining and processing of coal and other vital minerals while protecting the environment.
- There are more than 1,300 mine tailings impoundments in the United States.
- Mount Polley is a mine tailing dump of British Columbia, Canada.
-
Debris Control
- Dams provide enhanced environmental protection, such as the retention of hazardous materials and detrimental sedimentation. {adselite}
-
Navigation
- Dams and locks provide for a stable system of inland river transportation throughout the heartland of the Nation.
- Bonneville Dam of Washington, USA is a river navigation dam.
-
Recreation
- Dams provide prime recreational facilities throughout the United States. Boating, skiing, camping, picnic areas, and boat launch facilities are all supported by dams.
- Scrivener Dam is a recreation dam of Canberra, Australia.


Most of the dams are multipurpose. Almost all dams have at least some flood mitigation effect in addition to their primary purpose. Flood control dams may have some of their storage capacity kept empty to store excess water inflow under flood conditions.


.

