what is a dam - A dam is a hydraulic structure constructed across a river to store water on its upstream side. It is an impervious or fairly impervious barrier put across a natural stream so that a reservoir is formed.
Advantages of Dams
Dams are advantageous in different aspects. Dams ensure the benefits of improved health and life by supplying clean water, improved quality of sanitation, increased food (crop & fish) production, irrigation supply, protection of lives and goods from flood jeopardy, generation of electricity, tailings of mines and controlling the debris as well as the recreation and environmental benefits of the reservoirs. The detailed advantages of constructing a water dam are described below.
-
Irrigation

- For evapotranspiration crops and plants need irrigation. The huge amount of water reserved in dams is used for irrigation. Sustained supply of water for irrigation, encourages peoples to use additional areas for cropping. This enhances the increment of the food supply.
- Example: Burrinjuck Dam, an irrigation dam of Australia, which was built as the main headwater storage for the Murrumbidgee Irrigation Area in New South Wales.
-
Drinking-Water
- A portion of storage is withdrawn from reservoirs and supplied for drinking, municipal and industrial purposes. After proper treatment supplied water can be used for drinking. The water supply through dams enables people to drink pure water. This will prevent people from getting affected by water-borne diseases like cholera.
- Example: Warragamba, a water supply dam of Australia, supplies water to more than 3.7 million people living in Sydney and the lower Blue Mountains.
-
Electrical Generation
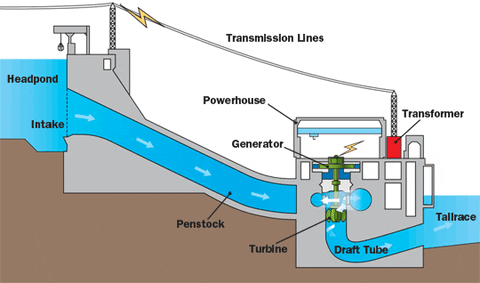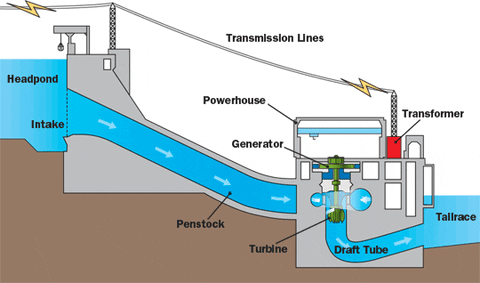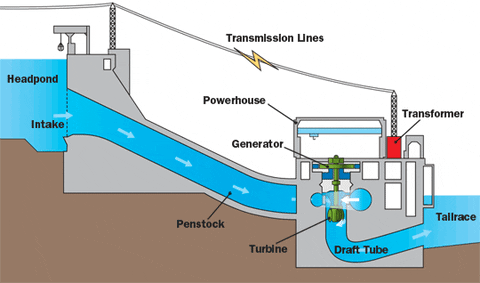
- Once constructed, electricity is generated from dams at a constant rate. The budget item of an electricity dam is least as there is no pricey fuel needed. Electricity dams additionally tend to last longer than thermal power plants. Hydropower generation is non-consumptive nature. Also, the resource is renewable and can be used again and again in the downstream for power generation. Thus, the use of stored or diverted waters for hydropower generation is considered most eco-friendly Example: In the United States, over 103,800 megawatts of electricity are produced from dams. Dams can also be formed in the sea where the tidal range is high and thus generate tidal power.
- Example: Itaipu Dam, a hydropower dam in Brazil, is the largest hydro-electric power station in the world.
-
Flood Control
{adselite}- During flood season, the flow of water in the downstream can be controlled by a dam. The reduction of the flood will save the crops and property from being washed away. It also reduces congestion of runoff in plains and coastal lands. Avoiding flood hazards can ensure the sustained economy of the whole country. It can be mentioned as the economic impacts of dams.
- Example: The Tennessee Valley Authority dams in the U.S.A., help to control floods on the Tennessee, the lower Ohio, and the lower Mississippi Rivers.
-
Mine Tailings
- Tailing dams are quite different from water dams. These dams are used to store the waste product from mining operations. Wastes from mining are called tailings. Tailings are very toxic. Dams can be used to store tailings to ensure the protection of the environment from being polluted.
- There are more than 1,300 mine tailings impoundments in the United States.
- Mount Polley is a mine tailing dump of British Columbia, Canada.
-
Water Storage
- The storage of water in reservoirs can be beneficial in many aspects. Upstream water ponds can be used for fish farming which can reduce the damage that has been done to the fish habitat due to the construction of the water dam.
- Example: Corin Dam is a Water Storage dam of Australia which has a capacity of 19.9×109 gal
-
Navigation
- Dams and locks provide for a stable system of inland river transportation throughout the heartland of the Nation.
- Bonneville Dam of Washington, USA is a river navigation dam.
-
Environment Friendly
- Reduce the emission of greenhouse gas e.g. carbon dioxide (CO2). Tailing dams help to protect the environment from getting contaminated by toxic mining wastes.
-
Debris Control
- Debris flows, often the result of environmental degradation in mountainous areas can be an extreme geological catastrophe. Detention dams are used to control the flow of hazardous materials and sediments.
-
Recreation
- Dam areas can be used for recreation purposes. Boating, skiing, camping, picnic areas, and boat launch facilities are all supported by water dams.
- Scrivener Dam is a recreation dam of Canberra, Australia.
Disadvantages of Dam:
Exact the opposite of advantages, dams also have some negative effects. One must know the problems of dams to have a clear idea on the effects of dams on humans, society, and environment. of dams such as:
- Submergence Problem: A large area gets submerged due to the rise in the water levels and turned into a reservoir. The owners of those lands have to be relocated, adequately compensated, and well settled somewhere else. This requires an extra budget for planning a dam construction.
- Failure of Dams: Dam failures may be caused either due to many reasons. Neglecting possible forces or unexpected forces is the main reason for the failure. The faulty design or occurrence of unanticipated floods can also be the cause of failure. Not maintaining proper guidelines during design and construction is also a reason for dam failures. Dams may sometimes fail due to excessive and unanticipated earthquakes. The failure of dams can bring enormous hazards to the life of people in that locality.
- Water wastage: Sometimes water used in excess of evapotranspiration requirements. This water appears in the system as surface or groundwater. But it degrades in quality, mainly due to fertilizers and pesticides, besides minerals drawn from soils. Such waste has to be minimized.
- Life cycles of habitats living in the water (like fish) get affected due to the construction of dams. Their life cycles are adapted to natural river habitat and flow regimes. By altering the flow, the physical surroundings are altered.
- Cycles and variation of flow downstream are established.
- Standing water (reservoir) habitats replace flowing water habitats.
- Nutrients are unable to procedure downstream.
- Coastal erosion is enhanced because of the loss of debris transportation.
- Productivity and species diversity of waterways are often reduced because of the reduction of fresh flow.
- A reduction in diversity happens.
We hope this article enlightens dam problems and solutions. We also hope that policymakers will consider environmental problems caused by dams during the construction of future dams.

