Foundations provide support to the structure and transfer the loads from the structure to the soil. However, the layer at which the foundation transfers the load shall have an adequate bearing capacity and suitable settlement characteristics. There are several types of foundations depending on various considerations such as
- Total load from the superstructure.
- Soil conditions.
- Water level.
- Noise and vibrations sensitivity.
- Available resources.
- The time frame of the project.
- Cost.
Broadly speaking, foundations can be classified as shallow foundations and deep foundations. Shallow footings are usually used when the bearing capacity of the surface soil is adequate to carry the loads imposed by a structure. On the other hand, different types of deep foundations are usually used when the bearing capacity of the surface soil is not sufficient to carry the loads imposed by a structure. So, the loads have to be transferred to a deeper level where the soil layer has a higher bearing capacity. A pile foundation is one of the deep foundation types. There is a huge interest among foundation engineers in piling in civil engineering. In this article, we will discuss pile foundation details along with the pile foundation definition.
What is a Pile Foundation?
A Pile foundation, a kind of deep foundation, can be defined as a slender column or long cylinder made of materials such as concrete or steel, which are used to support the structure and transfer the load a desired depth either by end bearing or skin friction.

Pile foundations are deep foundations. They are formed by long, slender, columnar elements typically made from steel or reinforced concrete, or sometimes timber. A foundation is described as 'piled' when its depth is more than three times its breadth.
Foundation piles are usually used for large structures and in situations where the soil at shallow depth is not suitable to resist excessive settlement, resist uplift, etc.
When to Use Pile Foundation
Often the question arises are the situations where pile foundation are suitable for. Following are the situations when using a pile foundation system can be beneficial.
- When the groundwater table is high foundation pilings are the best solution.
- Heavy and un-uniform loads from the superstructure are imposed.
- Other types of foundations are costlier or not feasible.
- When the soil at shallow depth is compressible.
- When there is the possibility of scouring, due to its location near the river bed or seashore, etc.
- When there is a canal or deep drainage system near the structure.
- When soil excavation is not possible up to the desired depth due to poor soil conditions.
- When it becomes impossible to keep the foundation trenches dry by pumping or by any other measure due to heavy inflow of seepage.
Whenever one of the above conditions occurs (where pile foundations are suitable for), the foundation engineer has to choose a foundation for the structure among different types of pile foundations.
Types of Pile Foundations
Piling foundations can be classified based on function, materials installation process, etc. The following are the types of pile foundations used in construction:
- Based on Function or Use
- Based on Materials and Construction Method
- Timber Piles
- Concrete Piles
- Steel Piles
- Composite Piles
The following diagram is representing different types of piles in construction discussed above.
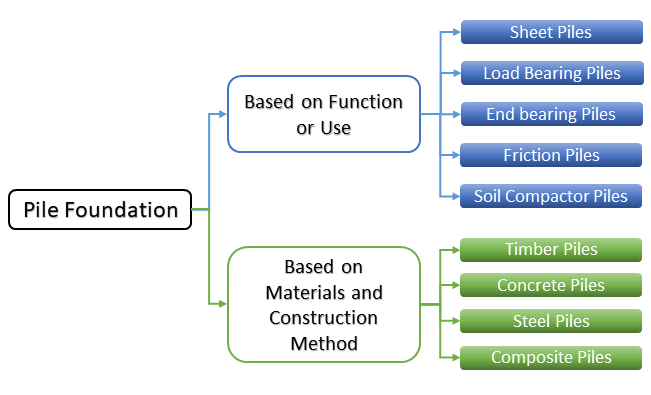
These pile foundation types are briefly discussed below.
Classification of Pile Foundation Based on Function or Use
As we can see in the following diagram, there are five pile types based on the uses and functions of piling foundations.
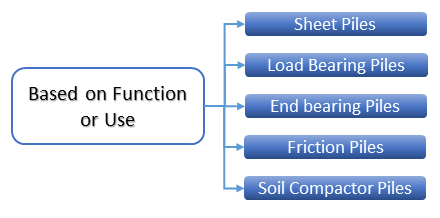
Sheet Piles
This type of pile is mostly used to provide lateral support. Usually, they resist lateral pressure from loose soil, the flow of water, etc. They are usually used for cofferdams, trench sheeting, shore protection, etc. They are not used for providing vertical support to the structure. They are usually used to serve the following purpose-
- Construction of retaining walls.
- Protection from river bank erosion.
- Retain the loose soil around the foundation trenches.
- For isolation of foundation from adjacent soils.
- For confinement of soil and thus increase the bearing capacity of the soil.
Load Bearing Piles
This type of building pile foundation is mainly used to transfer the vertical loads from the structure to the soil. These load-bearing pile foundations transmit loads through the soil with poor supporting property onto a layer that is capable of bearing the load. Depending on the mechanism of load transfer from pile to the soil, load-bearing piles can be further classified as flowed.
End Bearing Piles
In this type of pile foundation, the loads pass through the lower tip of the pile. The bottom end of the end-bearing piles rests on a strong layer of soil or rock. Usually, the pile rests at a transition layer of a weak and strong slayer. As a result, the pile acts as a column and safely transfers the load to the strong layer.
The total capacity of end-bearing pile foundation can be calculated by multiplying the area of the tip of the pile and the bearing capacity at that particular depth of soil at which the pile rests. Considering a reasonable factor of safety, the diameter of the pile is calculated.
Friction Pile
The Friction pile transfers the load from the structure to the soil by the frictional force between the surface of the pile and the soil surrounding the pile such as stiff clay, sandy soil, etc. Friction can be developed for the entire length of the pile or a definite length of the pile, depending on the strata of the soil. In friction piles, generally, the entire surface of the pile works to transfer the loads from the structure to the soil.
The surface area of the pile multiplied by the safe friction force developed per unit area determines the capacity of the pile.
While designing a skin friction pile, the skin friction to be developed at a pile surface should be sincerely evaluated and a reasonable factor of safety should be considered. Besides this one can increase the pile diameter, depth, and the number of piles and make the pile surface rough to increase the capacity of the friction pile.
Soil Compactor Piles
Unlike other pile foundation types, this type of pile does not carry any direct loads. This type of pile is driven at placed closed intervals to increase the bearing capacity of soil by compacting.
Types of Piles Based on Materials and Pile Foundation Construction Method
Primarily piles can be classified into two parts. Displacement piles and Non-displacement or Replacement piles. Piles that cause the soil to be displaced vertically and radially as they are driven to the ground are known as Displacement piles. In the case of Replacement piles, the ground is bored and the soil is removed and then the resulting hole is either filled with concrete or a pre-cast concrete pile is inserted. On the basis of materials of pile foundation construction and their installation process, load-bearing piles can be classified as follows:
- Timber Piles
- Untreated
- Treated with Preservative
- Concrete Piles
- Pre-cast Piles
- Cast-in-place Piles
- Steel Piles
- I-Section Piles
- Hollow Piles
- Composite Piles
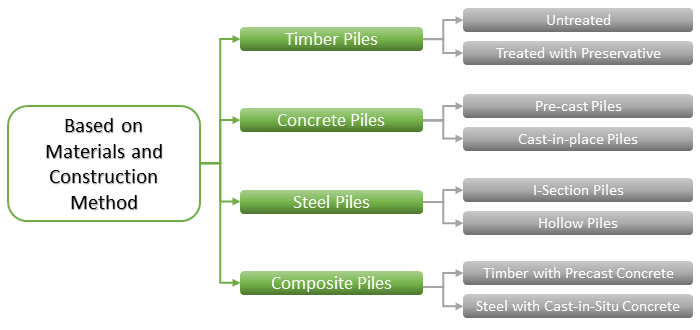
Timber Piles
Timber piles are the types of piled foundations that are placed under the water level. They last for approximately about 30 years. They can be rectangular or circular in shape. Their diameter or size can vary from 12 to 16 inches. The length of the pile is usually 20 times the top width.
They are usually designed for 15 to 20 tons. Additional strength can be obtained by bolting fish plates to the side of the piles.
Advantages of Timber Piles
- Timber piles of regular size are available.
- Economical.
- Easy to install.
- Low possibility of damage.
- Timber pile footings can be cut off at any desired length after they are installed.
- If necessary, timber piles can be easily pulled out.
Disadvantages of Timber Piles
- Piles of longer lengths are not always available.
- It is difficult to obtain straight piles if the length is short.
- It is difficult to drive the pile if the soil strata are very hard.
- Spicing of timber piles is difficult.
- Timber or wooden piles are not suitable to be used as end-bearing piles.
- For the durability of timber piles, special measures have to be taken. For example- wooden piles are often treated with preservatives.
Concrete Piles
Pre-cast Concrete Pile
The precast concrete pile foundation is cast in a pile bed in horizontal form if they are rectangular in shape. Usually, circular piles are cast in vertical forms. Precast piles are usually reinforced with steel to prevent breakage during their mobilization from the casting bed to the location of the foundation. After the piles are cast, curing has to be performed as per specification. Generally curing period for pre-cast piles is 21 to 28 days.
Advantages of Pre-cast Piles
- Provides high resistance to chemical and biological cracks.
- They are usually of high strength.
- To facilitate driving, a pipe may be installed along the center of the pile.
- If the piles are cast and ready to be driven before the installation phase is due, it can increase the pace of work.
- The confinement of the reinforcement can be ensured.
- The quality of the pile can be controlled.
- f any fault is identified, it can be replaced before driving.
- Pre-cast piles can be driven under the water.
- The piles can be loaded immediately after it is driven up to the required length.
Disadvantages of Pre-cast Piles
- Once the length of the pile is decided, it is difficult to increase or decrease the length of the pile afterward.
- They are difficult to mobilize.
- Needs heavy and expensive equipment to drive.
- As they are not available for readymade purchase, it can cause a delay in the project.
- There is a possibility of breakage or damage during the handling and driving of piles.
Cast-in-Place Concrete Piles
This type of pile footing is constructed by boring soil up to the desired depth and then, depositing freshly mixed concrete in that place and letting it cure there. cast in situ concrete pile foundation is constructed either by driving a metallic shell to the ground and filling it with concrete and leaving the shell with the concrete or the shell is pulled out while concrete is poured. Usually, round piles are used in cast-in-situ piling.
Advantages of Cast-in-Place Concrete Piles Foundation
- The shells are lightweight, so they are easy to handle.
- The length of piles can be varied easily.
- The shells may be assembled at sight.
- No excess enforcement is required only to prevent damage from handling.
- No possibility of breaking during installation.
- Additional piles can be provided easily if required.
Disadvantages of Cast-in-Place Concrete Piles
- In this type of pile foundation, installation requires careful supervision and quality control.
- Needs sufficient place on site for storage of the materials used for construction.
- It is difficult to construct cast in situ piles where the underground water flow is heavy.
- The bottom of the pile may not be symmetrical.
- If the pile is un-reinforced and uncased, the pile can fail in tension if there acts an uplifting force.
Steel Piles
Steel piles may be of I-section or hollow pipe. They are filled with concrete. The size may vary from 10 inches to 24 inches in diameter and the thickness is usually ¾ inches. Because of the small sectional area, the piles are easy to drive. They are mostly used as end-bearing piles.
Advantages of Steel Piles
- They are easy to install.
- They can reach a greater depth compared to any other type of pile foundations.
- Can penetrate through the hard layer of soil due to the less cross-sectional area.
- It is easy to splice steel piles
- Can carry heavy loads.
Disadvantages of Steel Piles
- This piling type is prone to corrosion.
- Has a possibility of deviating while driving.
- Comparatively expensive.
Pile Foundation Articles
- What is Pile Foundation? Types of Pile Foundation
- Uses of Pile Foundation
- Pile foundation advantages and disadvantages
- Factors Affecting Selection of Pile Foundation Type
- Causes of Pile Foundation Failure
- Difference Between Shallow and Deep Foundation
- What is Friction Pile? Capacity Calculation & Details
- Differences Between Pile and Pier Foundation
- Difference Between Piles, Piers, and Caissons

